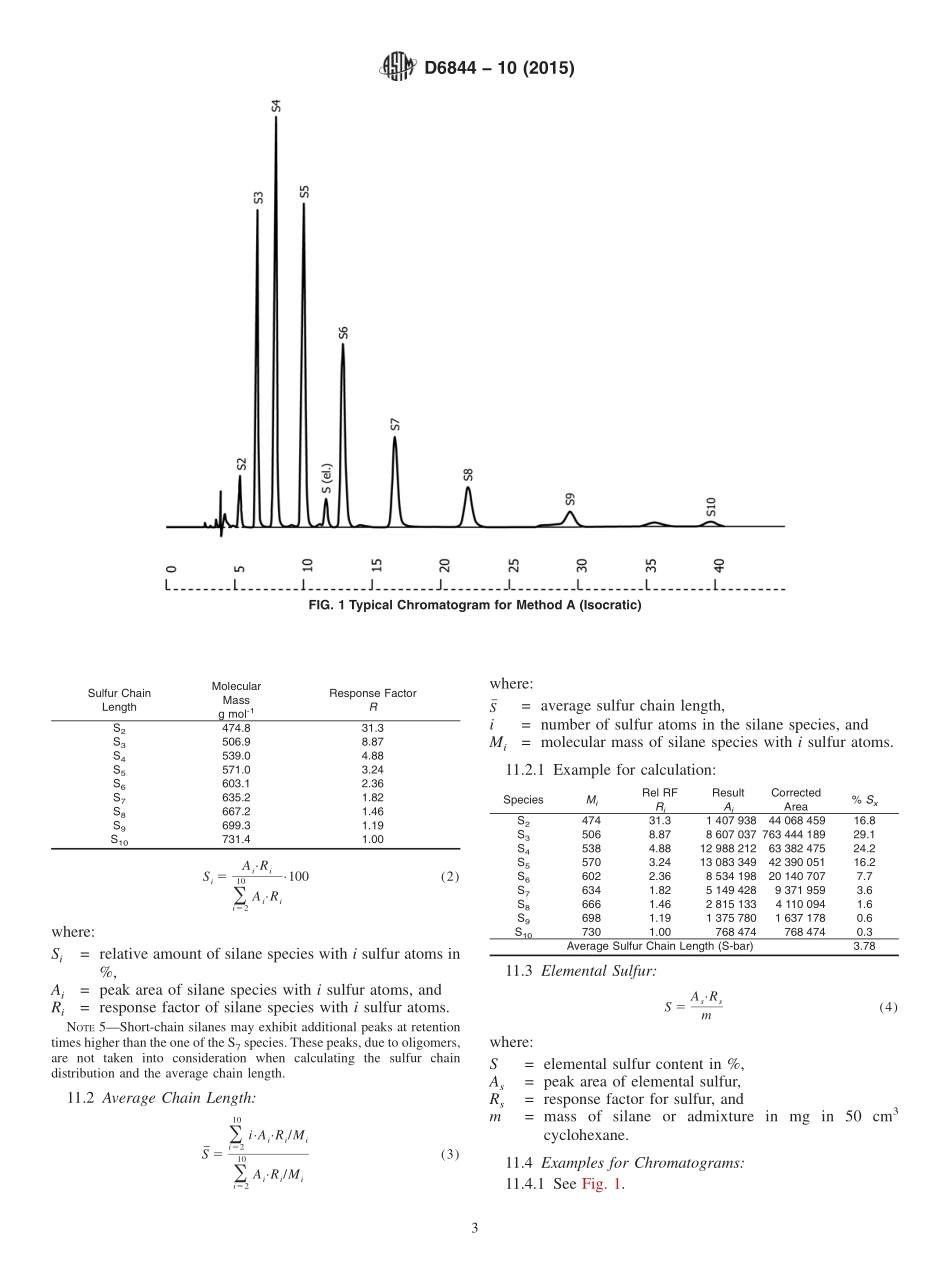
Designation:D6844−10(Reapproved2015)StandardTestMethodforSilanesUsedinRubberFormulations(bis-(triethoxysilylpropyl)sulfanes):CharacterizationbyHighPerformanceLiquidChromatography(HPLC)1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD6844;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversthecharacterizationofsilanes,orofadmixturesofsilaneandcarbonblack(see10.4),ofthetypebis-(triethoxysilylpropyl)sulfanebyhighperformanceliquidchromatography.1.2ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D5297TestMethodsforRubberChemicalAccelerator—PuritybyHighPerformanceLiquidChromatographyE177PracticeforUseoftheTermsPrecisionandBiasinASTMTestMethodsE682PracticeforLiquidChromatographyTermsandRela-tionshipsE691PracticeforConductinganInterlaboratoryStudytoDeterminethePrecisionofaTestMethod3.Terminology3.1Definitions:3.1.1Sx—Bis-(triethoxysilylpropyl)polysulfaneorpolysulfide,(EtO)3SiC3H6SxC3H6Si(OEt)33.1.2S2—Bis-(triethoxysilylpropyl)disulfaneordisulfide,(EtO)3SiC3H6S2C3H6Si(OEt)33.1.3S3—Bis-(triethoxysilylpropyl)trisulfaneortrisulfide,(EtO)3SiC3H6S3C3H6Si(OEt)33.1.4S3—Bis-(triethoxysilylpropyl)tetrasulfaneortetrasulfide,(EtO)3SiC3H6S4C3H6Si(OEt)33.1.5S3—Bis-(triethoxysilylpropyl)pentasulfaneorpentasulfide,(EtO)3SiC3H6S5C3H6Si(OEt)33.1.6S3—Bis-(triethoxysilylpropyl)hexasulfaneorhexasulfide,(EtO)3SiC3H6S6C3H6Si(OEt)33.1.7S3—Bis-(triethoxysilylpropyl)heptasulfaneorheptasulfide,(EtO)3SiC3H6S7C3H6Si(OEt)33.1.8S3—Bis-(...