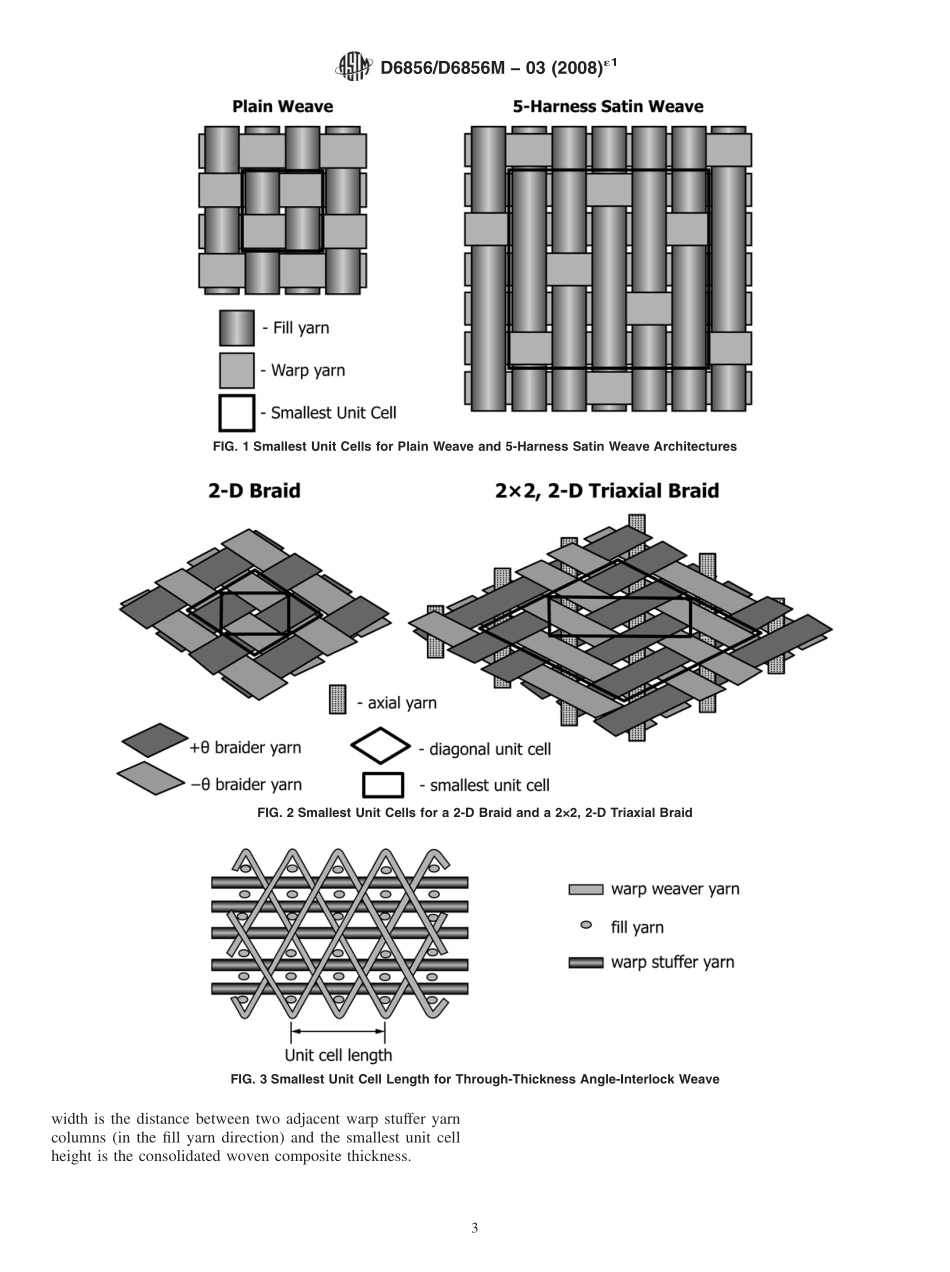
Designation:D6856/D6856M−03(Reapproved2008)´1StandardGuideforTestingFabric-Reinforced“Textile”CompositeMaterials1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD6856/D6856M;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.ε1NOTE—EditoriallychangedtoacombinedstandardinSeptember2010.INTRODUCTIONAvarietyoffabric-reinforcedcompositematerialshavebeendevelopedforuseinaerospace,automotive,andotherapplications.Thesecompositematerialsarereinforcedwithcontinuousfiberyarnsthatareformedintotwo-dimensionalorthree-dimensionalfabrics.Variousfabricconstructions,suchaswoven,braided,stitched,andsoforth,canbeusedtoformthefabricreinforcement.Duetothenatureofthereinforcement,thesematerialsareoftenreferredtoas“textile”composites.Textilecompositescanbefabricatedfrom2-dimensional(2-D)or3-dimensional(3-D)fabrics.Stitchedpreformsand3-Dfabricscontainthrough-thicknessyarns,whichcanleadtogreaterdelaminationresistance.Textilecompositesarealsoamenabletoautomatedfabrication.However,themicrostructure(orfiberarchitecture)ofatextilecomposite,whichconsistsofinterlacingyarns,canleadtoincreasedinhomogeneityofthelocaldisplacementfieldsinthelaminate.Dependinguponthesizeoftheyarnsandthepatternoftheweaveorbraid,theinhomogeneitywithinatextilecompositecanbelargecomparedtotraditionaltapelaminates.Thus,specialcareshouldbeexercisedintheuseofthecurrentASTMstandardsdevelopedforhighperformancecomposites.Inmanycases,thecurrentASTMstandardsarequiteadequateifproperattentionisgiventothespecialtestingconsiderationsfortextilecompositescoveredinthisguide.However,insomecases,currentstandardsdonotmeettheneedsfortestingoftherequiredproperties.Thisguideisintendedtoincreasetheuser’sawarenessofthespecialconsiderationsnecessaryforthetestingofthesematerials.ItalsoprovidestheuserwithrecommendedASTMstandardsthatareappl...