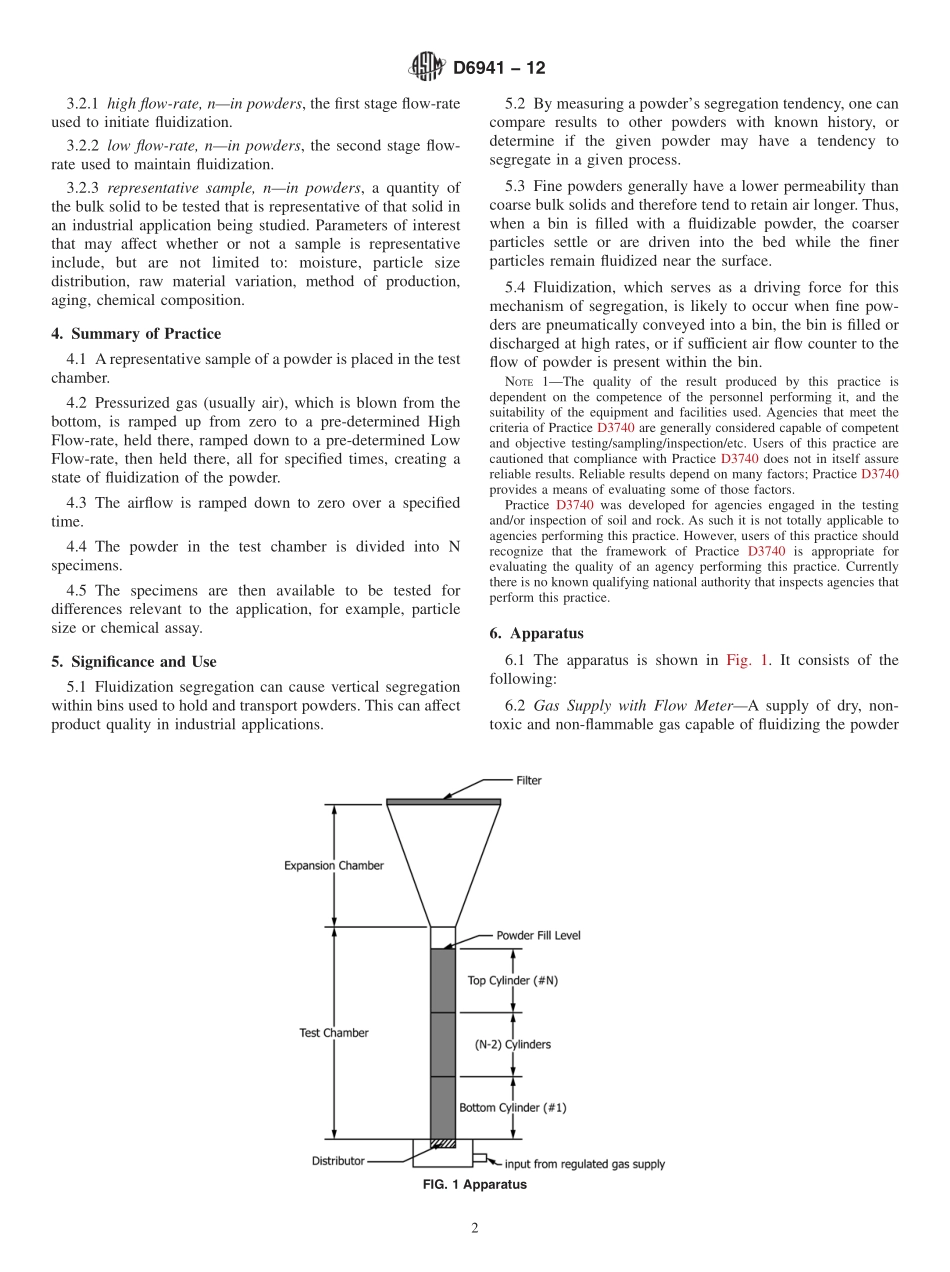
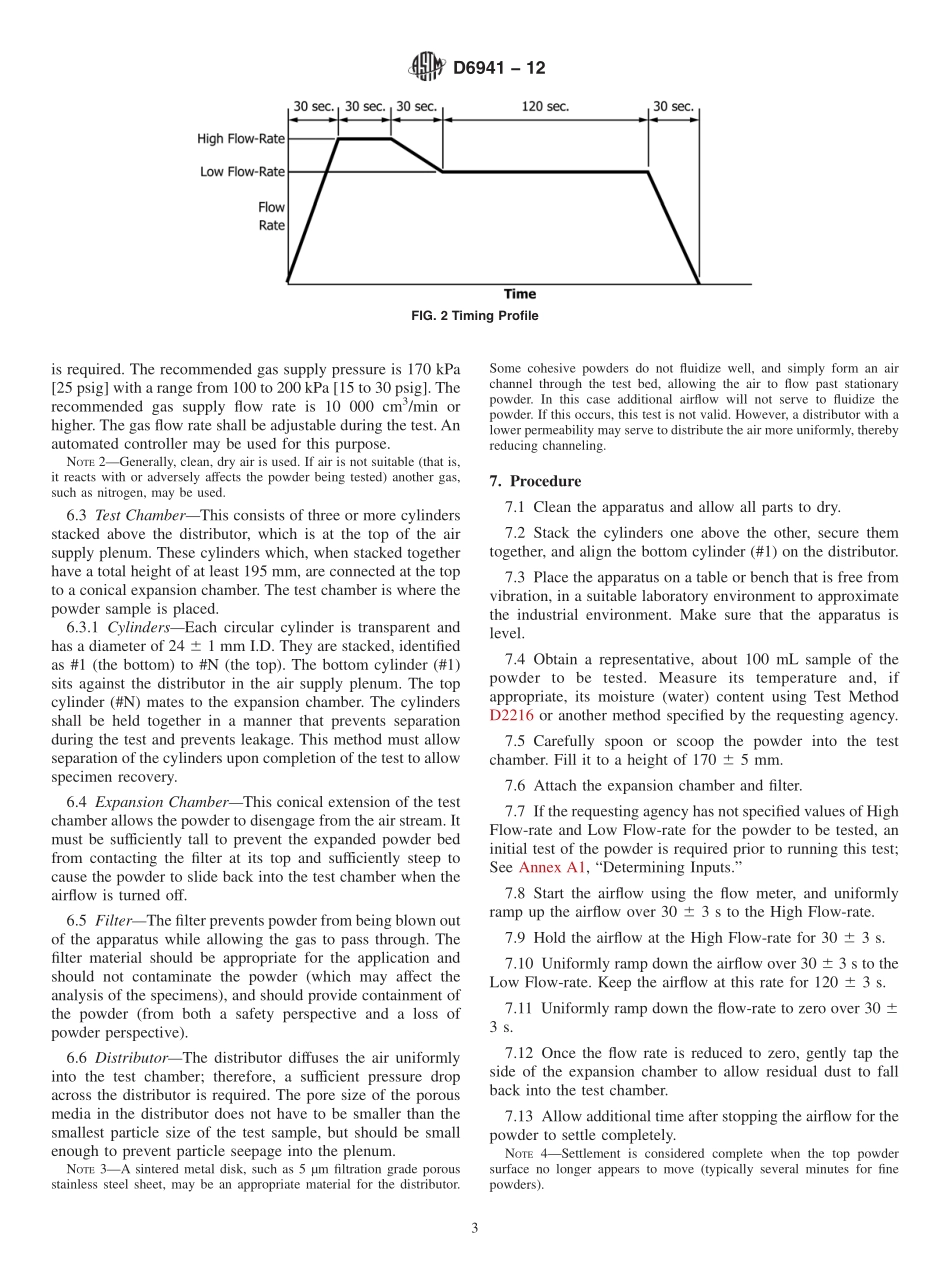
Designation:D6941−12StandardPracticeforMeasuringFluidizationSegregationTendenciesofPowders1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD6941;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope*1.1Thispracticecoversanapparatusandprocedureforcreatingseveralspecimensofapowdersamplethat,ifthepowderisonethatsegregatesbythefluidizationmechanism,shouldbedifferentfromoneanother.1.2Apowdersampleisfluidizedthen,afterthefluidizinggasisturnedoff,itisseparatedintothreeormorespecimensthatcanbeanalyzedforparametersofinterest.Thedifferenceintheseparametersbetweenthespecimensisanindicationofthesegregationpotentialofthepowder.1.3Powdersmustbecapableofbeingfluidizedinordertobetestedbythispractice.1.4Temperature-andmoisture-sensitivepowdersmayneedtobetestedatdifferenttemperaturesandmoisturecontents,aswouldhappeninanindustrialenvironment.1.5Thisstandardisnotapplicabletoallbulksolidsandsegregationmechanisms:whilefluidizationisacommonsegregationmechanismexperiencedbymanyfinepowders,othersegregationmechanismsnotevaluatedbythisstandardmightinducesegregationinpractice.PracticeD6940coversanothercommonmechanism:sifting.1.6Theextenttowhichsegregationwilloccurinanindustrialsituationisnotonlyafunctionofthepowderanditstendencytosegregate,butalsothehandlingequipment(forexample,bindesign),process(forexample,transferrates),andenvironment.1.7ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.8Thispracticeoffersasetofinstructionsforperformingoneormorespecificoperations.Thisdocumentcannotreplaceeducationorexperienceandshouldbeusedinconjunctionwithprofessionaljudgment.Notallaspectsofthispracticemaybeapplicableinallcircumstances.ThisASTMstandardisnotintendedtorepresentorreplacethestandardofcarebywhichtheadequacyofagivenprofessionalservicemus...