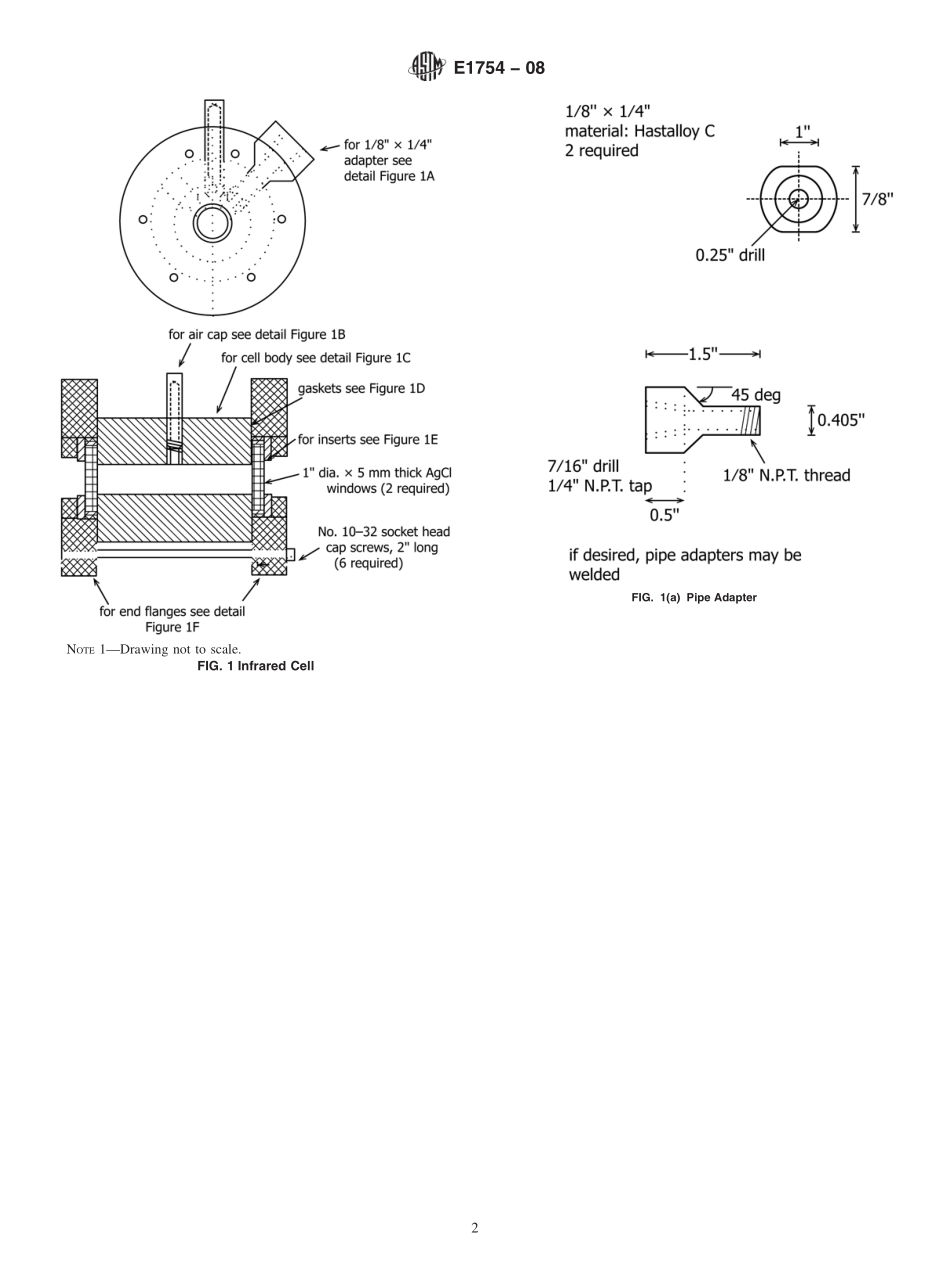
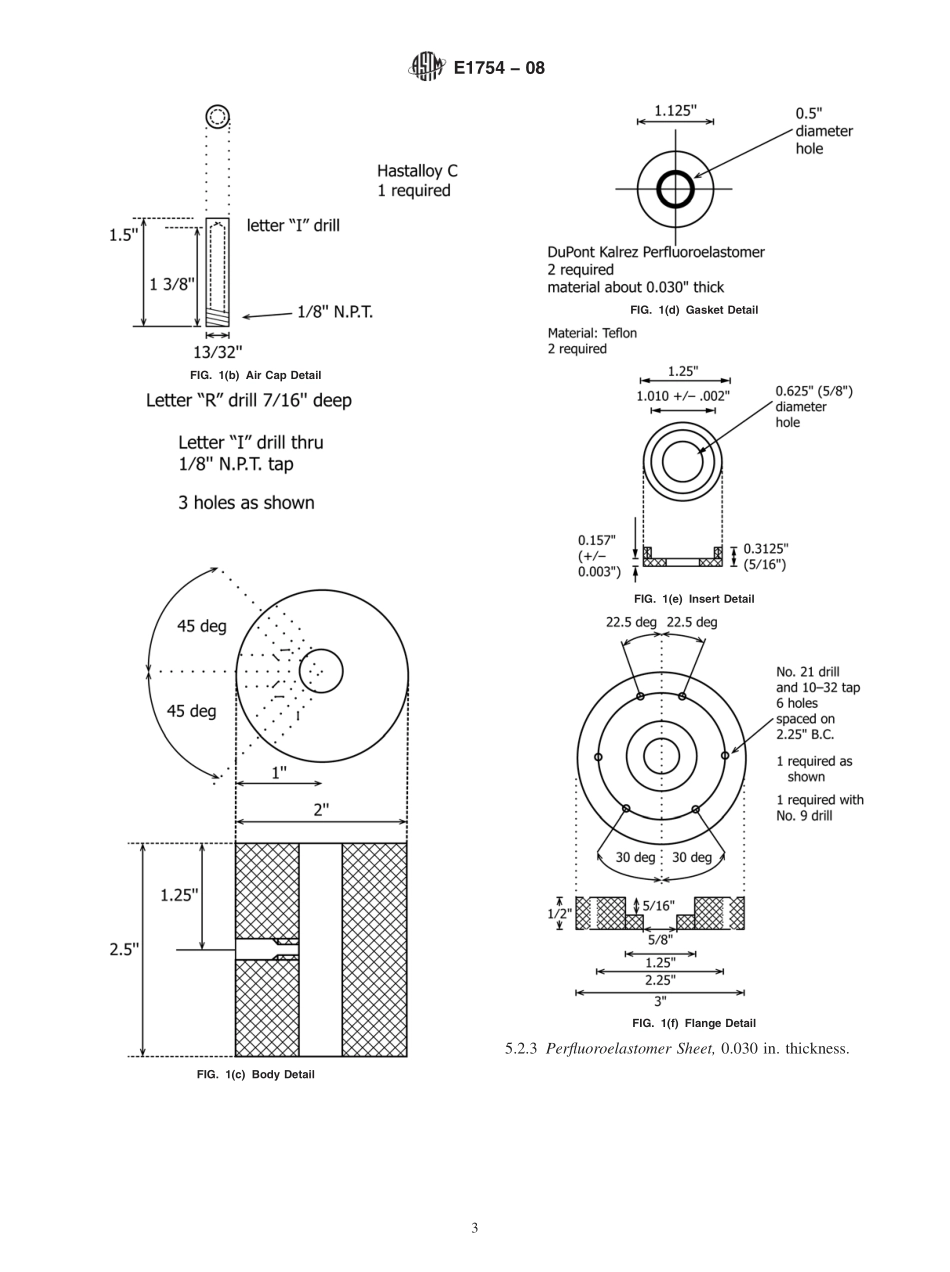
Designation:E1754−08StandardTestMethodforDeterminationofLowLevelsofWaterinLiquidChlorineByInfraredSpectrophotometry1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationE1754;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope*1.1Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofthecontentofwaterinliquidchlorineintheconcentrationrangeof0.5to15mg/kg(ppm).1.2ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesareforinformationonly.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.SeeSection7forspecifichazardsstatements.1.4ReviewthecurrentMaterialSafetyDataSheets(MSDS)fordetailedinformationconcerningtoxicity,firstaidprocedures,andsafetyprecautions.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D1193SpecificationforReagentWaterE806TestMethodforCarbonTetrachlorideandChloroforminLiquidChlorinebyDirectInjection(GasChromato-graphicProcedure)2.2FederalStandards:349CFR173CodeofFederalRegulationsTitle49Trans-portation:Shippers’GeneralRequirementsforShipmentsandPackaging,includingSections:173.304ChargingofCylinderswithLiquefiedCompressedGas173.314RequirementsforCompressedGasesinTankCars173.315CompressedGasesinCargoTanksandPortableTankContainers3.SummaryofTestMethod3.1Asampleofliquidchlorineisintroducedintoaspecialinfraredcellandmaintainedasaliquidunderitsownpressure.Aspectrometerscansfrom400to4400wavenumbersoftheinfraredtransmissionspectrumofliquidchlorine.Thisspec-trumisthenratioedtooneobtainedofthenitrogen-filledinfraredcellpreviously.Theratioedspectrumisconvertedtoabsorbance,andthenetabsorbanceofthewaterbandat1596wavenumbers,relativetoareferenceat1663wavenumbers,isdetermined.T...