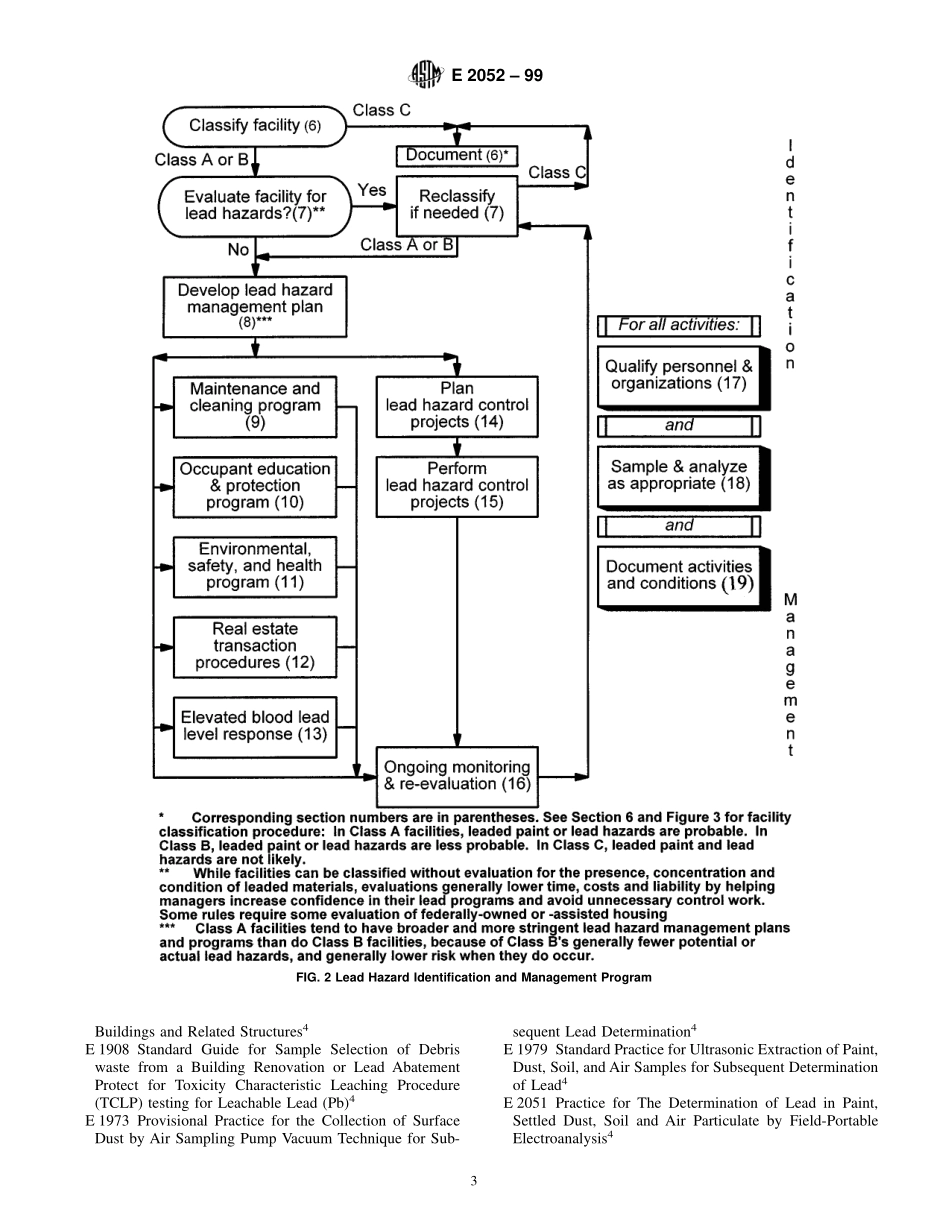
Designation:E2052–99StandardGuideforEvaluation,Management,andControlofLeadHazardsinFacilities1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationE2052;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(e)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1ThisguideprovidesdetailedguidanceforusebyownersandpropertymanagersindevelopingandimplementingaleadhazardmanagementprograminfacilitiesthatarelikelytobeoccupiedorvisitedbychildrenundersixorbypregnantwomenbyprovidinganorganizedapproachtousingASTMandotherstandards.Itspurposeistoprotectoccupants,visitors,staff,otherworkers,andtheenvironmentfromleadhazardsinthesefacilities.1.1.1Fig.1providesanoverviewofthemajorleadhazardidentificationandmanagementprogramelements.1.1.2Fig.2providesanoutlineoftheleadhazardidentifi-cationandmanagementprogramprocess.1.2Limitations:1.2.1Thisprovisionalguidedoesnotapplytofacilitiesthatarenotlikelytobeoccupiedorvisitedbychildrenundersix,orbypregnantwomen.Itdoesnotapplytooccupationalexposuresotherthanthoseresultingfrommaintenance,clean-ing,leadhazardcontrolwork,andotherrenovationandrepairworkthatgeneratesleadhazards.1.2.2Thisguideisbasedonfederalandnationalstandardsandguidelinesthatmaybedifferentfromapplicablestateandlocalregulations.Itdoesnot,however,comprehensivelyad-dressOSHA,EPA,orDOTrequirements.Itmaynotprotectallusers,oroccupants,visitors,staff,otherworkers,andtheenvironmentaffectedbytheirfacilitiesfromleadhazards.Usersmustcomplywithapplicablelawsandregulationsandmodifytheguidanceprovidedbythisguideaccordingly.Theuserisadvisedtoadoptthemoststringentversionofeachrequirementamongfederal,state,andlocalregulations.1.3Executionofworkdiscussedorrecommendedinthisguidemaycauseexposuretoconstructionsafetyandhealthhazards,tohealthhazardsfromleadinpaint,dust,andbaresoil,andtohealthhazardsfromproductsandmethodsassoci-atedwithleadhazardcontrol.Thi...