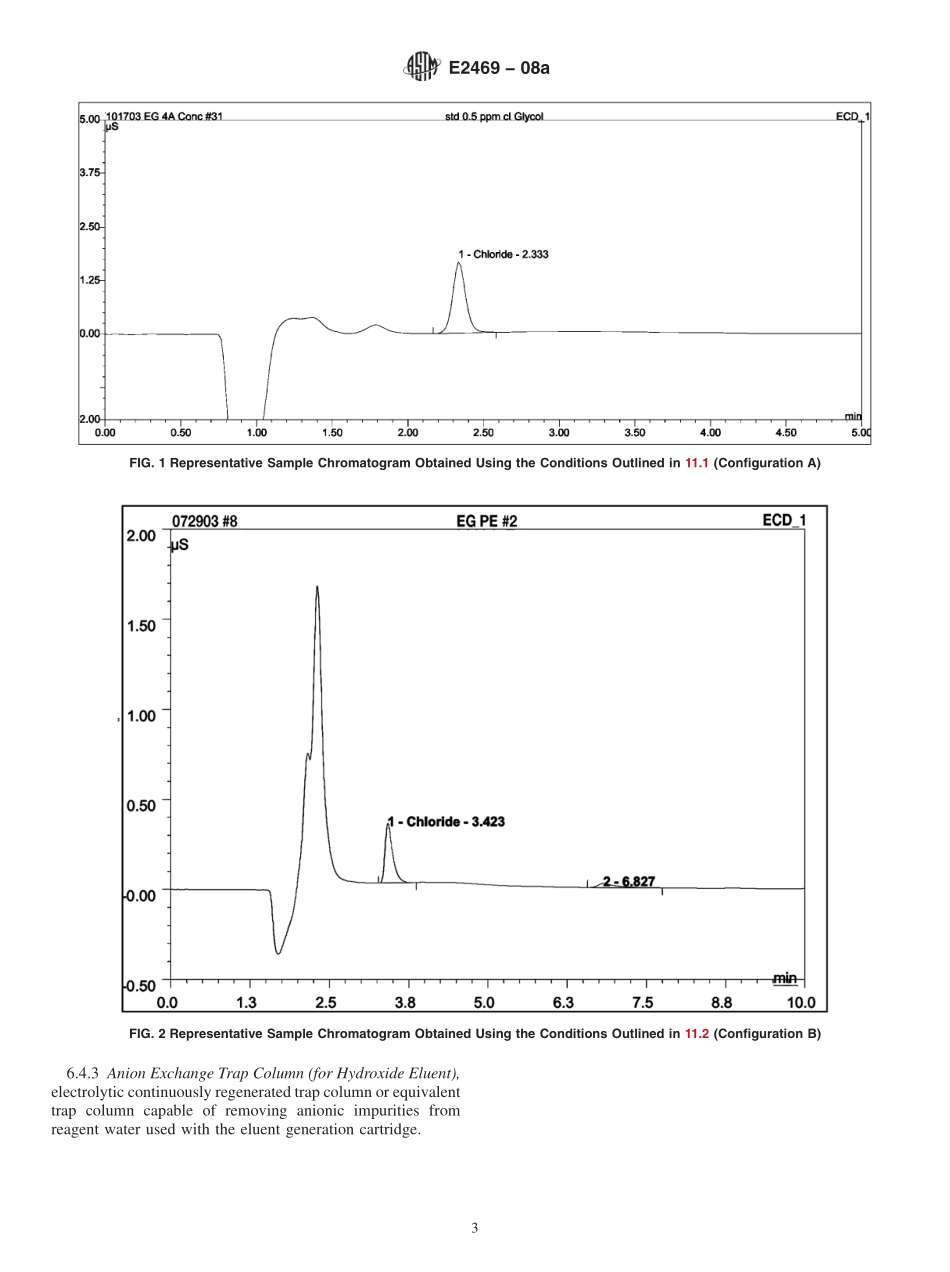
Designation:E2469−08aStandardTestMethodforChlorideinMono-,Di-andTri-ethyleneGlycolbyIonChromatography1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationE2469;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope*1.1Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofinorganicchloride(chlorideion)inmonoethyleneglycol(MEG),dieth-yleneglycol(DEG)andtriethyleneglycol(TEG)intherangeof0.01to1.0mg/kgbyionchromatography(IC).1.2Ethyleneglycolcanbeanalyzeddirectlybythistestmethodwithoutanysamplepreparationordilutedwithhighqualitydeionizedwaterifanautosamplerisusedanddilutionisnecessary(thatis,50:50orothersuitableratio).1.3ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.3.1Theexceptionistheadditionalinformationof(psi)in9.3.3.1.4ReviewthecurrentMaterialSafetyDataSheets(MSDS)fordetailedinformationconcerningtoxicity,first-aidproce-duresandsafetyprecautions.1.5Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesandtodeterminetheapplicabilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.Forspecifichazardstatements,seeSection9.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D1193SpecificationforReagentWaterE180PracticeforDeterminingthePrecisionofASTMMethodsforAnalysisandTestingofIndustrialandSpe-cialtyChemicals(Withdrawn2009)3E300PracticeforSamplingIndustrialChemicals3.SummaryofTestMethod3.1Analiquotoftheglycolsampleisinjecteddirectly(manually)ordiluted(viaautosampler)intoanionchromato-graphconsistingofaninjectorwithafixedsampleloop,twoanionexchangecolumns(guardandseparatorcolumn),ananionsuppressorandaconductivitydetector.Ionsaresepa-ratedbasedontheiraffinityfortheionexchangesitesoftheresinwithrespecttotheresin’saffinityfortheeluent.Th...