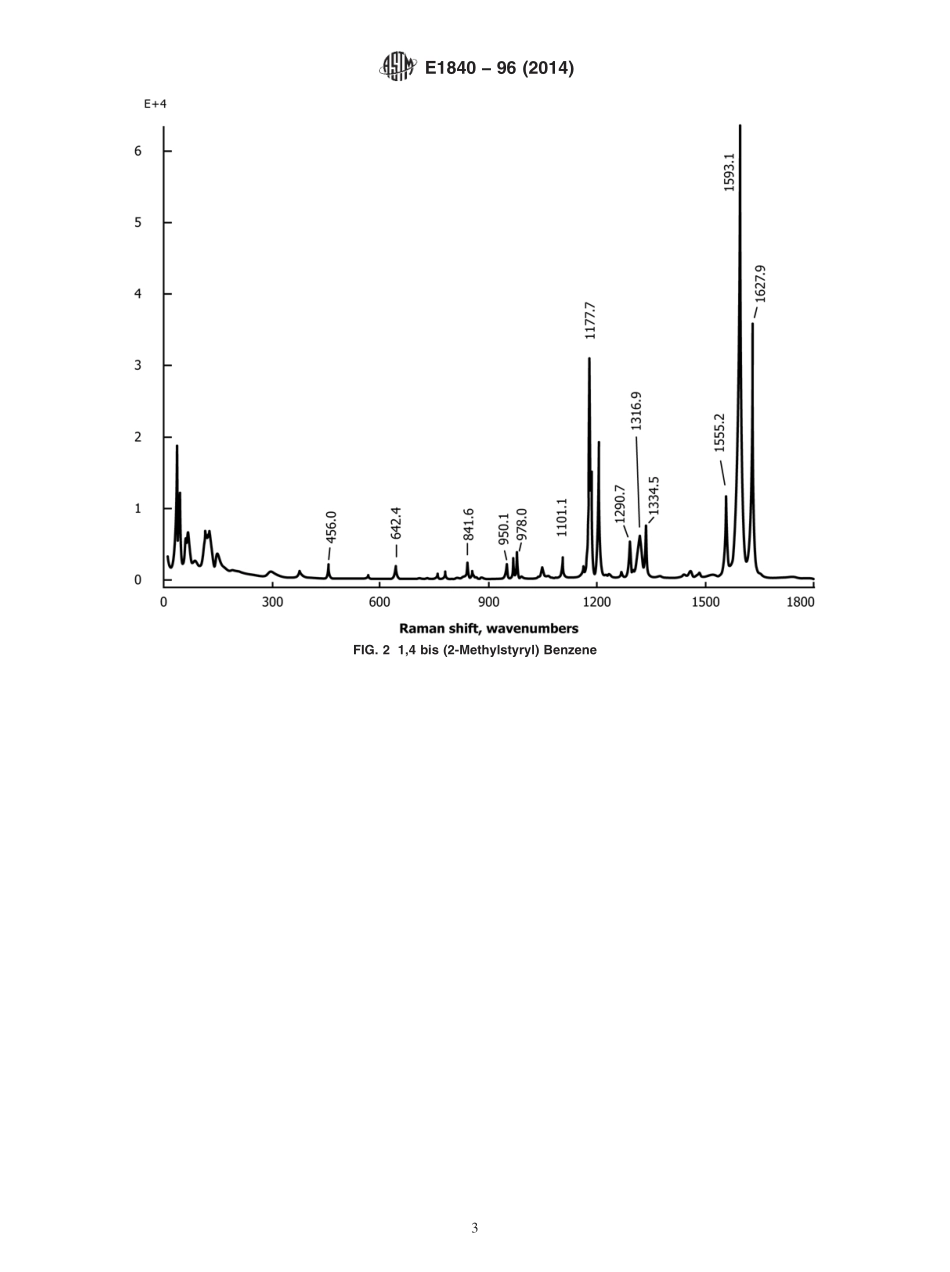
Designation:E1840−96(Reapproved2014)StandardGuideforRamanShiftStandardsforSpectrometerCalibration1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationE1840;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1ThisguidecoversRamanshiftvaluesforcommonliquidandsolidchemicalsthatcanbeusedforwavenumbercalibrationofRamanspectrometers.TheguidedoesnotincludeproceduresforcalibratingRamaninstruments.Instead,thisguideprovidesreliableRamanshiftvaluesthatcanbeusedasacomplementtolow-pressurearclampemissionlineswhichhavebeenestablishedwithahighdegreeofaccuracyandprecision.1.2ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.3Someofthechemicalsspecifiedinthisguidemaybehazardous.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisguidetoconsultmaterialsafetydatasheetsandotherpertinentinfor-mationtoestablishappropriatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplicabilityofregulatorylimitationspriortotheiruse.1.4Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2E131TerminologyRelatingtoMolecularSpectroscopyE1683PracticeforTestingthePerformanceofScanningRamanSpectrometers3.Terminology3.1Definitions—TerminologyusedinthisguideconformstothedefinitionssetforthinTerminologyE131.4.SignificanceandUse4.1WavenumbercalibrationisanimportantpartofRamananalysis.ThecalibrationofaRamanspectrometerisperformedorcheckedfrequentlyinthecourseofnormaloperationandevenmoreoftenwhenworkingathighresolution.Todate,themostcommonsourceofwavenumbervaluesiseitheremissionlinesfromlow-pressuredischargelamps(forexample,mercury,argon,orneon)orfromthenon...