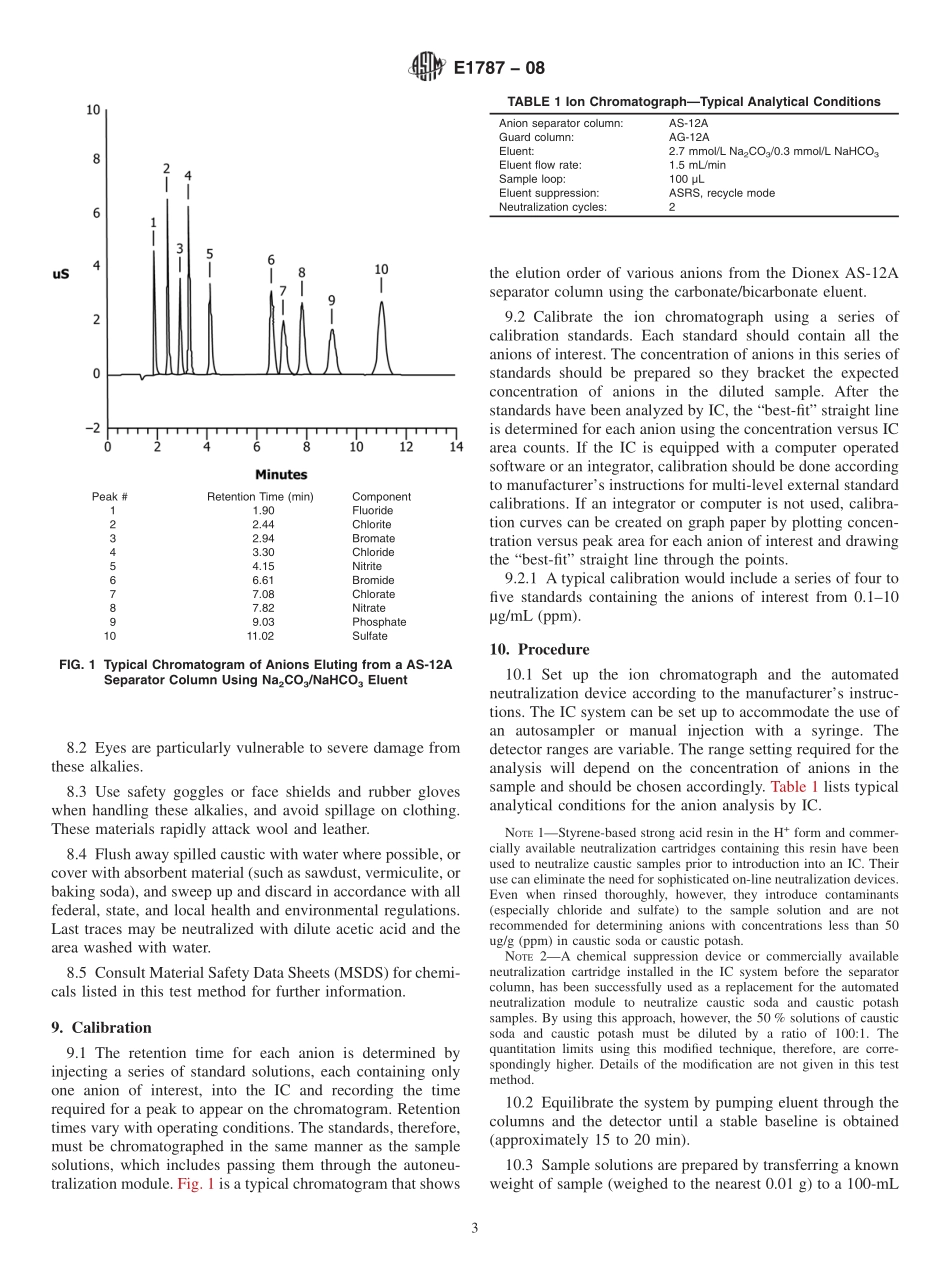
Designation:E1787−08StandardTestMethodforAnionsinCausticSodaandCausticPotash(SodiumHydroxideandPotassiumHydroxide)byIonChromatography1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationE1787;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope*1.1Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofanionicimpuritiesin50%causticsoda(sodiumhydroxide)and50%causticpotash(potassiumhydroxide)solutionsusingionchromatography(IC).Anionsthatcanbedeterminedatcon-centrationsofapproximately0.1–1000ug/g(ppm)include:bromide,chlorate,chloride,fluoride,nitrate,phosphate,andsulfate.1.2Byvaryingthesamplesize,thistestmethodcanbeusedforanhydrouscausticsodaandcausticpotashproducts,aswellasotherconcentrationsofliquidproducts.1.3Thistestmethodisnotintendedtobeusedtoquantifychlorideincausticsodawherethesodiumchlorideconcentra-tionisapproximately1%.Forthemostaccuratedeterminations,itisrecommendedthathighconcentrationsofchloridebeanalyzedusingapotentiometrictitrationprocedure,suchastheonedescribedinTestMethodsE291.1.4ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesareforinformationonly.1.5ReviewthecurrentappropriateMaterialSafetyDataSheets(MSDS)fordetailedinformationconcerningtoxicity,firstaidprocedures,andsafetyprecautions.1.6Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.SpecifichazardsstatementsaregiveninSection8.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D1193SpecificationforReagentWaterE180PracticeforDeterminingthePrecisionofASTMMethodsforAnalysisandTestingofIndustrialandSpe-cialtyChemicals(Withdrawn2009)3E291TestMethodsforChemicalAnalysisofCausticSodaandCausticPotash(SodiumHydroxide...