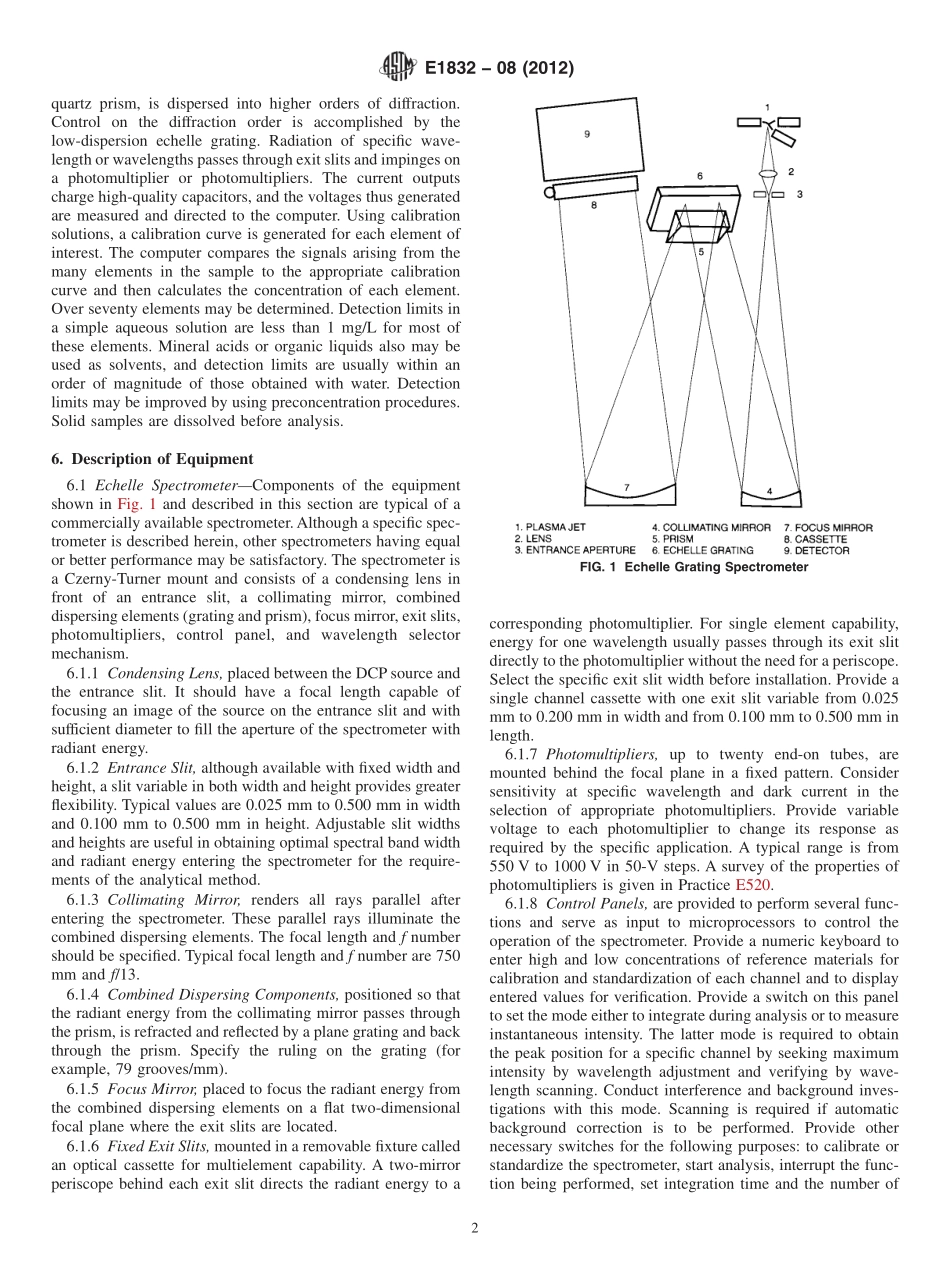
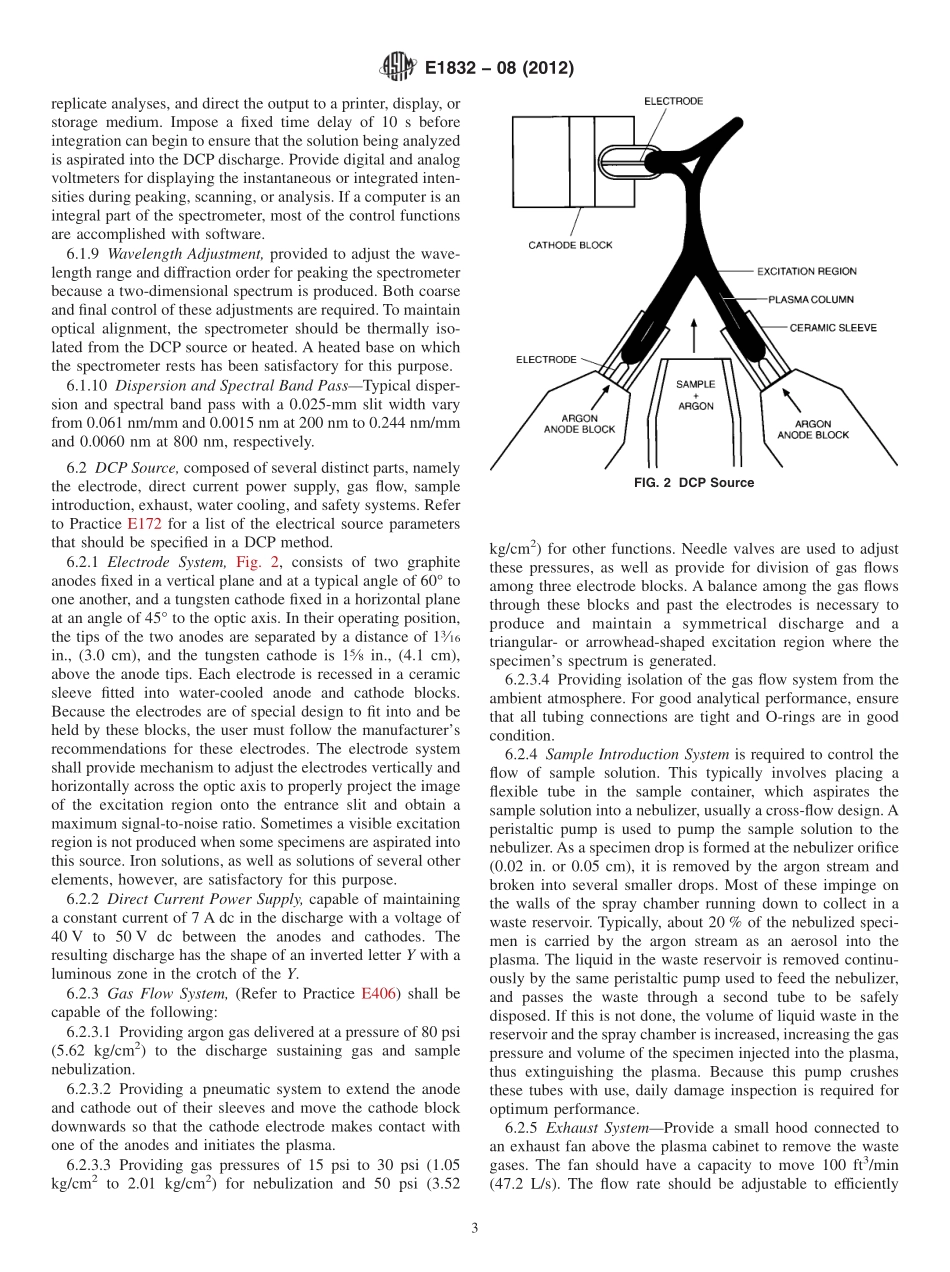
Designation:E1832−08(Reapproved2012)StandardPracticeforDescribingandSpecifyingaDirectCurrentPlasmaAtomicEmissionSpectrometer1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationE1832;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thispracticedescribesthecomponentsofadirectcurrentplasma(DCP)atomicemissionspectrometer.Thispracticedoesnotattempttospecifycomponenttolerancesorperformancecriteria.Thispracticedoes,however,attempttoidentifycriticalfactorsaffectingbias,precision,andsensitivity.Aprospectiveusershouldconsultwiththevendorbeforeplacinganordertodesignatestingprotocolfordemonstratingthattheinstrumentmeetsallanticipatedneeds.1.2Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.SpecifichazardsstatementsaregiveinSection9.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2E135TerminologyRelatingtoAnalyticalChemistryforMetals,Ores,andRelatedMaterialsE158PracticeforFundamentalCalculationstoConvertIntensitiesintoConcentrationsinOpticalEmissionSpec-trochemicalAnalysis(Withdrawn2004)3E172PracticeforDescribingandSpecifyingtheExcitationSourceinEmissionSpectrochemicalAnalysis(Withdrawn2001)3E406PracticeforUsingControlledAtmospheresinSpec-trochemicalAnalysisE416PracticeforPlanningandSafeOperationofaSpec-trochemicalLaboratory(Withdrawn2005)3E520PracticeforDescribingPhotomultiplierDetectorsinEmissionandAbsorptionSpectrometryE528PracticeforGroundingBasicOpticalEmissionSpec-trochemicalEquipment(Withdrawn1998)3E1097GuideforDeterminationofVariousElementsbyDirectCurrentPlasmaAtomicEmissionSpectrometry3.Terminology3.1Forterminologyrelatingtoemissionspectrometry,refertoTerminologyE135.4.Significancea...