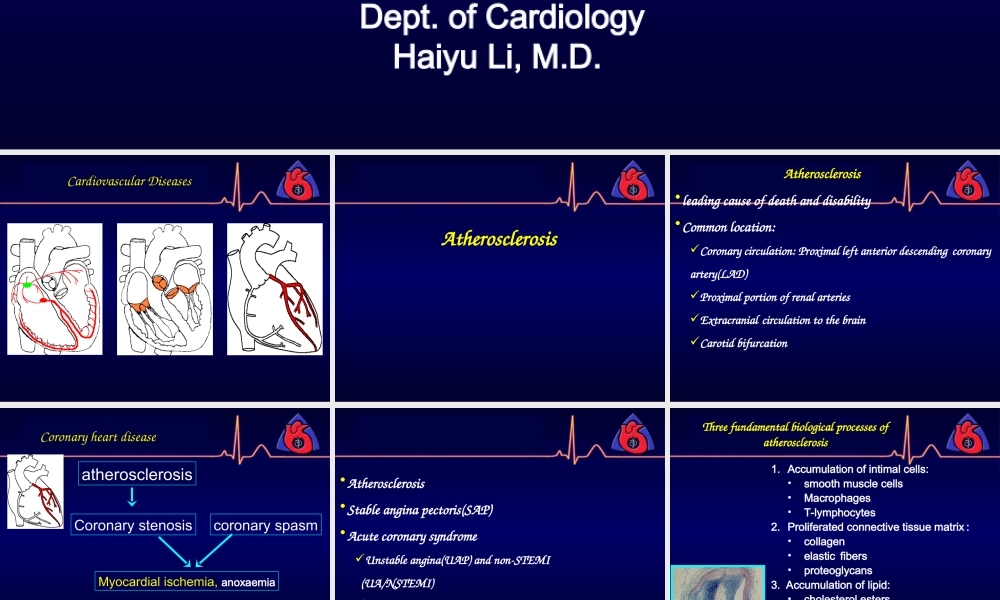
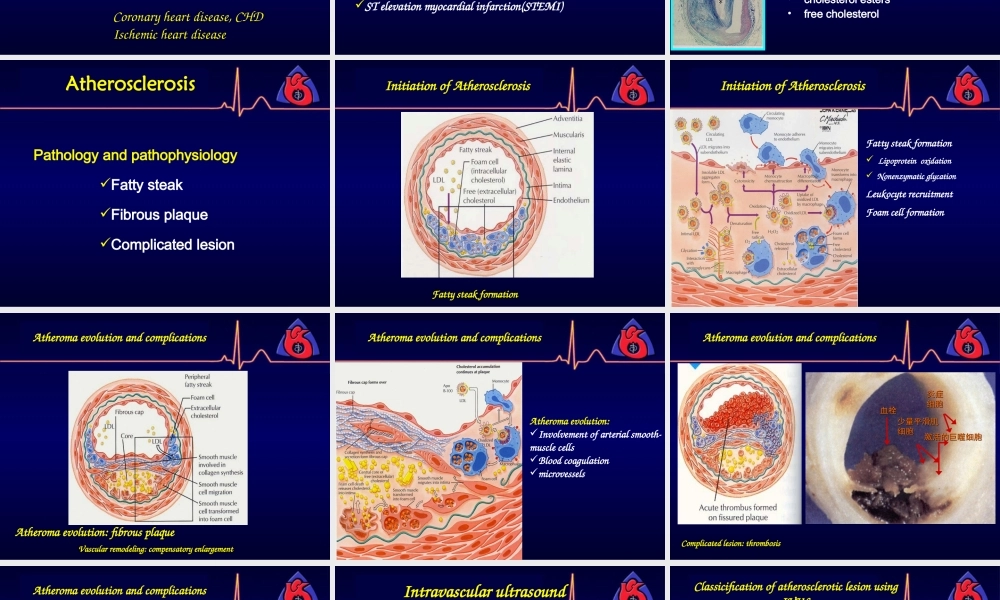
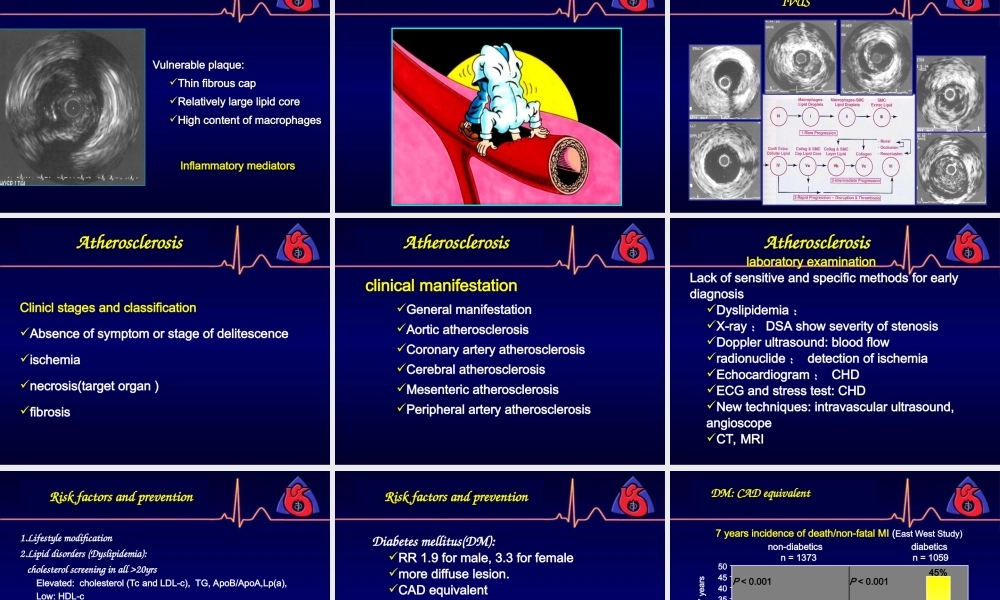
Atherosclerosis&CoronaryheartdiseasesZhengzhouUniversity,FirstaffiliatedHospitalDept.ofCardiologyHaiyuLi,M.D.CardiovascularDiseasesAtherosclerosis•leadingcauseofdeathanddisability•Commonlocation:Coronarycirculation:Proximalleftanteriordescendingcoronaryartery(LAD)ProximalportionofrenalarteriesExtracranialcirculationtothebrainCarotidbifurcationAtherosclerosisCoronaryheartdiseaseatherosclerosisCoronarystenosiscoronaryspasmMyocardialischemia,anoxaemiaCoronaryheartdisease,CHDIschemicheartdisease•Atherosclerosis•Stableanginapectoris(SAP)•AcutecoronarysyndromeUnstableangina(UAP)andnon-STEMI(UA/NSTEMI)STelevationmyocardialinfarction(STEMI)Threefundamentalbiologicalprocessesofatherosclerosis1.Accumulationofintimalcells:•smoothmusclecells•Macrophages•T-lymphocytes2.Proliferatedconnectivetissuematrix:•collagen•elasticfibers•proteoglycans3.Accumulationoflipid:•cholesterolesters•freecholesterolPathologyandpathophysiologyFattysteakFibrousplaqueComplicatedlesionAtherosclerosisInitiationofAtherosclerosisFattysteakformationInitiationofAtherosclerosisFattysteakformationLipoproteinoxidationNonenzymaticglycationLeukocyterecruitmentFoamcellformationAtheromaevolution:fibrousplaqueAtheromaevolutionandcomplicationsVascularremodeling:compensatoryenlargementVascularremodeling:compensatoryenlargementAtheromaevolution:Involvementofarterialsmooth-musclecellsBloodcoagulationmicrovesselsAtheromaevolutionandcomplications炎症炎症细胞细胞少量平滑肌少量平滑肌细胞细胞激活的巨噬细胞激活的巨噬细胞血栓血栓Complicatedlesion:thrombosisAtheromaevolutionandcomplicationsAtheromaevolutionandcomplicationsVulnerableplaque:Vulnerableplaque:ThinfibrouscapThinfibrouscapRelativelylargelipidcoreRelativelylargelipidcoreHighcontentofmacrophagesHighcontentofmacrophagesInflammatorymediatorsInflammatorymediatorsIntravascularultrasoundClassicificationofatheroscleroticlesionusingIVUSCliniclstagesandclassificationAbsenceofsymptomorstageofdelitescenceischemianecrosis(ta...