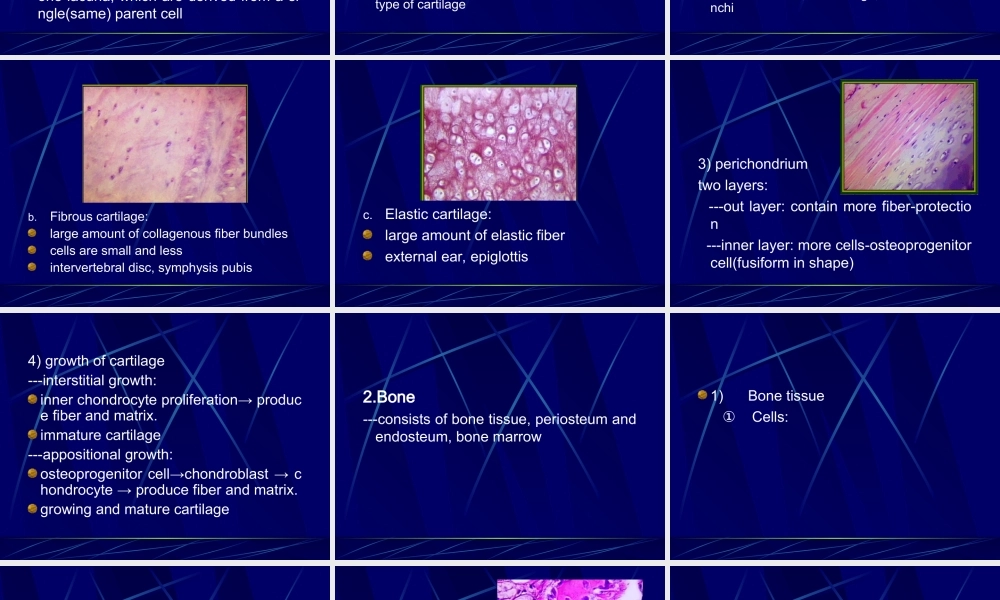
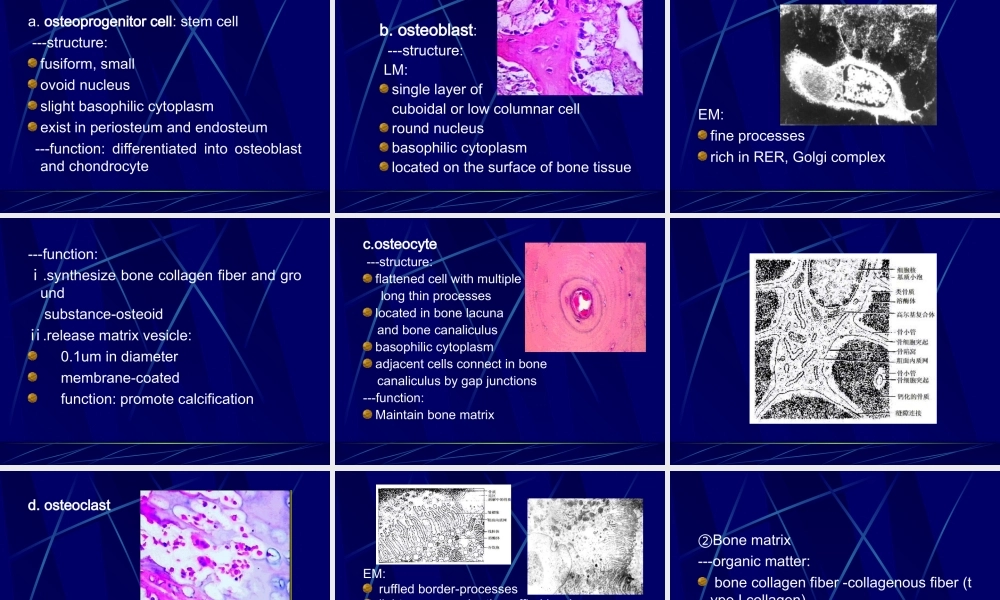
CartilageandBone1.Cartilage:organ=Cartilagetissue+perichondrium1)structureofcartilagetissue---cell:chondrocyte---cartilagematrix①chondrocyte:---Structure:LMembeddedincartilagelacunaperipheralcells:--smallandimmature--singleandflattenedcentralcell:--largeandmature,--roundandingroupof2-8cells--smallandroundnucleus--basophiliccytoplasm--EM:richinRERandGolgicomplex*isogenousgroup:severalcellslocatesinonelacuna,whicharederivedfromasingle(same)parentcell②Cartilagematrix---groundsubstance:proteoglycan:--sametolooseCT--therearemorechondroitinsulfatedistributedattheperipheryofcartilagelacuna---calledascartilagecapsule(basophilic)water---fiber:typeandnumberoffiberdependsonthetypeofcartilage2)Classification:accordingtothefibera.Hyalinecartilage:lesscollagenousfibrilarticularsurface,ribcartilage,tracheaandbronchib.Fibrouscartilage:largeamountofcollagenousfiberbundlescellsaresmallandlessintervertebraldisc,symphysispubisc.Elasticcartilage:largeamountofelasticfiberexternalear,epiglottis3)perichondriumtwolayers:---outlayer:containmorefiber-protection---innerlayer:morecells-osteoprogenitorcell(fusiforminshape)4)growthofcartilage---interstitialgrowth:innerchondrocyteproliferation→producefiberandmatrix.immaturecartilage---appositionalgrowth:osteoprogenitorcell→chondroblast→chondrocyte→producefiberandmatrix.growingandmaturecartilage2.Bone---consistsofbonetissue,periosteumandendosteum,bonemarrow1)Bonetissue①Cells:a.osteoprogenitorcell:stemcell---structure:fusiform,smallovoidnucleusslightbasophiliccytoplasmexistinperiosteumandendosteum---function:differentiatedintoosteoblastandchondrocyteb.osteoblast:---structure:LM:singlelayerofcuboidalorlowcolumnarcellroundnucleusbasophiliccytoplasmlocatedonthesurfaceofbonetissueEM:fineprocessesrichinRER,Golgicomplex---function:ⅰ.synthesizebonecollagenfiberandgroundsubstance-osteoidⅱ.releasematrixvesicle:0.1umindiametermembrane-coatedfunction:promotecalcificationc.osteocyte---structure:flattenedcellwithmultiplelongthinprocesseslocatedinbone...