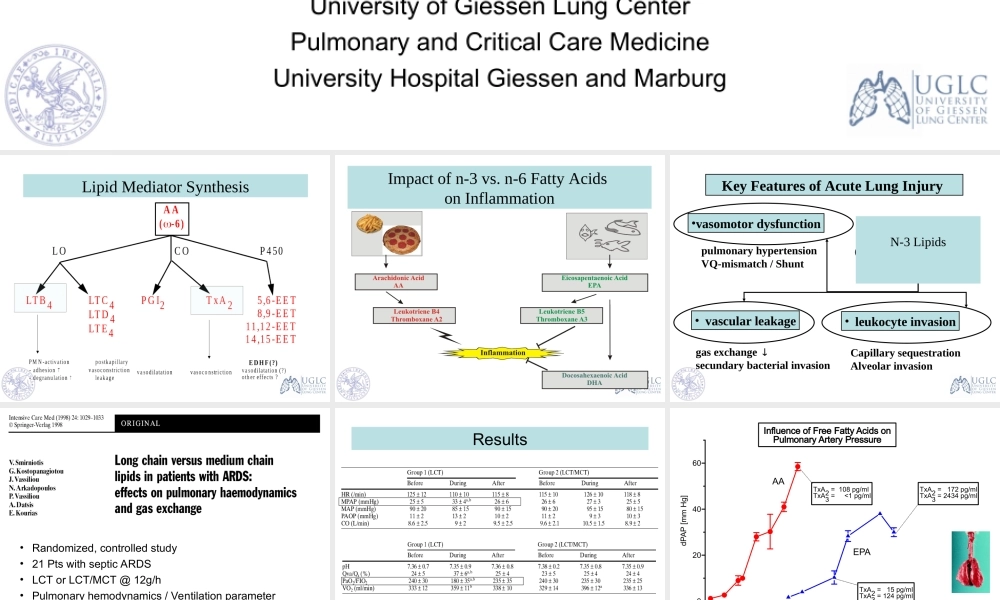
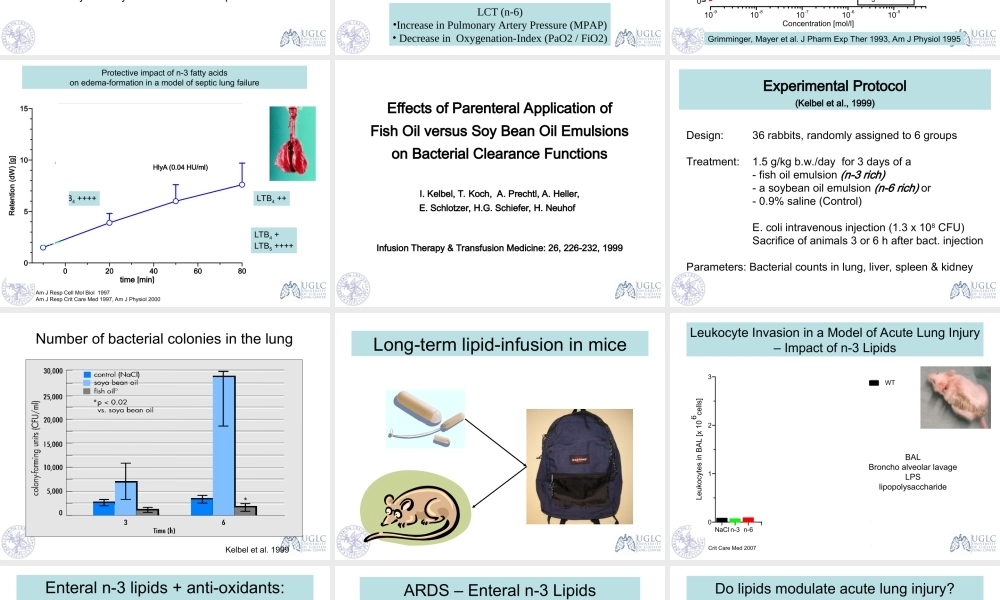
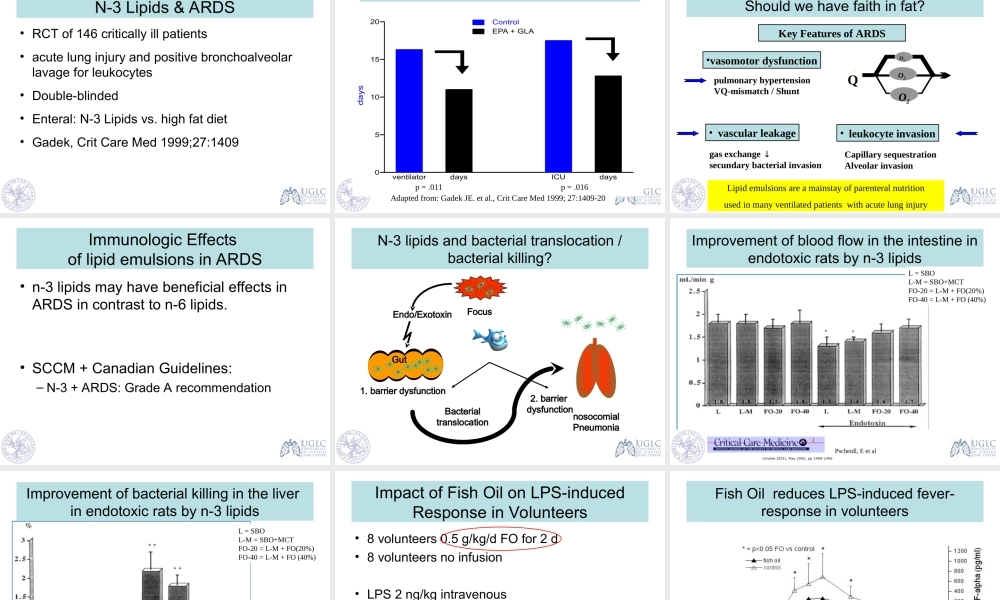
N-3LipidsinCriticalCareMedicineDr.KonstantinMayerUniversityofGiessenLungCenterPulmonaryandCriticalCareMedicineUniversityHospitalGiessenandMarburgLipidMediatorSynthesisImpactofn-3vs.n-6FattyAcidsonInflammationKeyFeaturesofAcuteLungInjurypulmonaryhypertensionVQ-mismatch/Shunt•vasomotordysfunction•vascularleakagegasexchangesecundarybacterialinvasionQO2O2O2•leukocyteinvasionCapillarysequestrationAlveolarinvasionN-3Lipids•Randomized,controlledstudy•21PtswithsepticARDS•LCTorLCT/MCT@12g/h•Pulmonaryhemodynamics/VentilationparameterResultsLCT(n-6)•IncreaseinPulmonaryArteryPressure(MPAP)•DecreaseinOxygenation-Index(PaO2/FiO2)0204060dPAP[mmHg]10-910-810-710-610-5Concentration[mol/l]InfluenceofFreeFattyAcidsonPulmonaryArteryPressureTxA2=108pg/mlTxA3=<1pg/mlTxA2=172pg/mlTxA3=2434pg/mlTxA2=15pg/mlTxA3=124pg/mlAAEPAF.Grimmingeretal,JPharmacolExpTher,1993,267:259-265F.Grimmingeretal,AmJPhysiol.1995,268:H2252-H2259Grimminger,Mayeretal.JPharmExpTher1993,AmJPhysiol1995AmJRespCellMolBiol1997AmJRespCritCareMed1997,AmJPhysiol2000051015Retention(dW)[g]020406080time[min]HlyA(0.04HU/ml)HlyA+200nMEPAHlyA+100nMAA(dW>60g)InfluenceofFreeFattyAcidsonVascularLeakageinaSepticLungModelF.Grimmingeretal,AmJRespCritCareMed,1997,155:513-9Protectiveimpactofn-3fattyacidsonedema-formationinamodelofsepticlungfailureLTB4++++LTB4++LTB4+LTB5++++EffectsofParenteralApplicationofFishOilversusSoyBeanOilEmulsionsonBacterialClearanceFunctionsI.Kelbel,T.Koch,A.Prechtl,A.Heller,E.Schlotzer,H.G.Schiefer,H.NeuhofInfusionTherapy&TransfusionMedicine:26,226-232,1999ExperimentalProtocol(Kelbeletal.,1999)Design:36rabbits,randomlyassignedto6groupsTreatment:1.5g/kgb.w./dayfor3daysofa-fishoilemulsion(n-3rich)-asoybeanoilemulsion(n-6rich)or-0.9%saline(Control)E.coliintravenousinjection(1.3x108CFU)Sacrificeofanimals3or6hafterbact.injectionParameters:Bacterialcountsinlung,liver,spleen&kidneyNumberofbacterialcoloniesinthelungKelbeletal.1999Long-termlipid-infusioninmiceLeukocyteInvasioninaModelofAcuteLungInjury–Impac...